From Antimony to Zinc, your body needs minerals. Zinc is key to hundreds of important functions, including sugar and protein metabolism, DNA formation and energy production. It’s also needed for proper growth and development, and it helps strengthen your immune system.
- Supports immune function
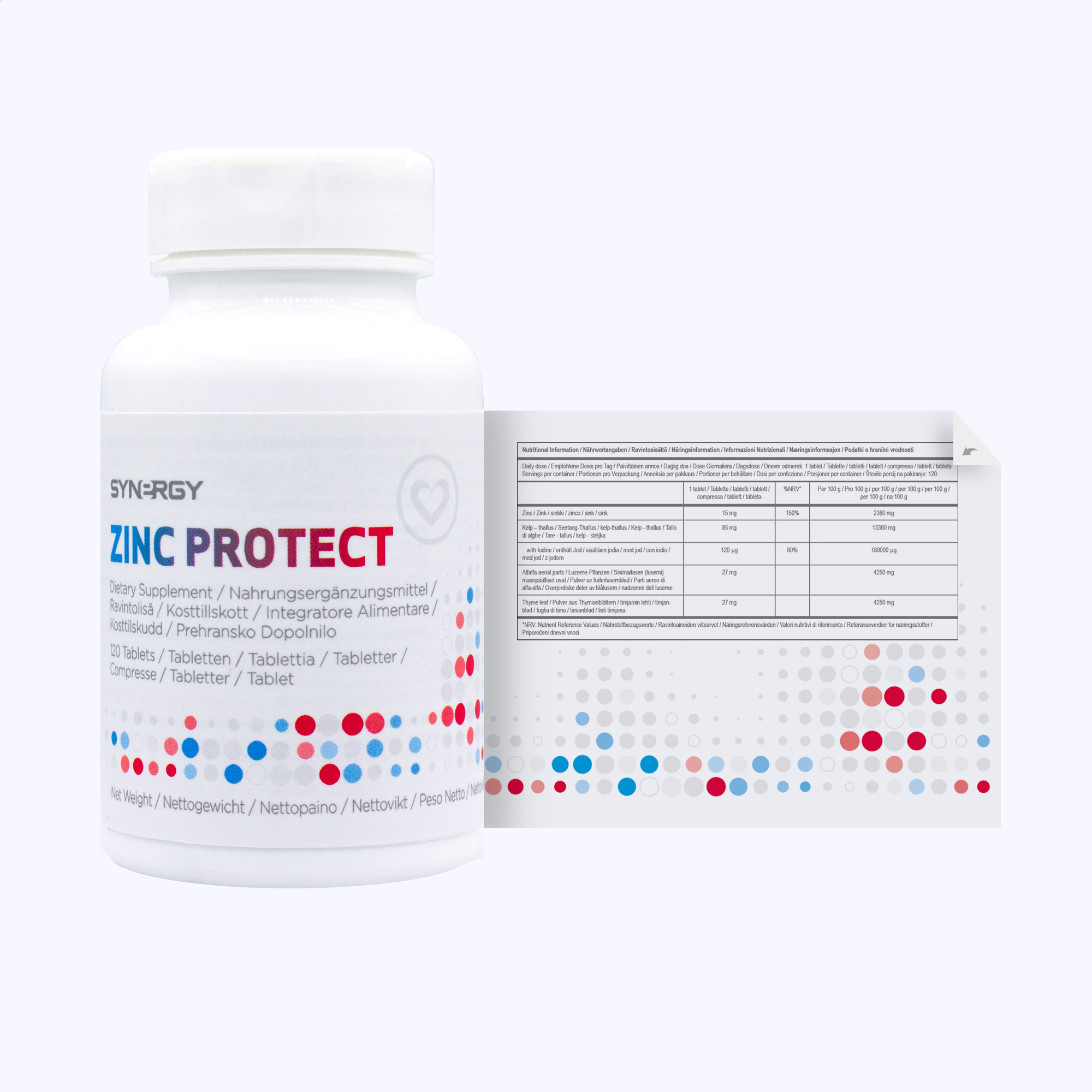
- 15 mg Zinc per tablet
The Story behind Zinc
It wasn’t until 1961 that researchers discovered the importance of zinc to the diet. Zinc deficiency can affect a host of systems, including the nervous, skeletal, immune, and reproductive systems. It can also affect the function of the GI tract and the skin.
Why Our Zinc?
Purity. Our zinc raw material contains no phthalates, allergens, or animal derivatives. It’s also free from carcinogens and toxins. It’s certified Kosher and Halal. Our partner in the mineral business is, like us, committed to excellence, safety, and purity. Their ingredients prove to be consistently pure every time. And their US manufacturing facilities are cGMP certified.
Zinc
Zinc is a trace mineral with many functions and benefits. It supports the immune system, plays a role in metabolism, and contributes to normal cognitive function. Zinc also assists with taste and smell.
Research shows that zinc can support multiple parts of the immune system. Zinc is vital for the development and function of cells that support innate immunity. Zinc deficiency is associated with impaired function of these cells.
Zinc may also be linked to skin health. Zinc contributes to the maintenance of normal vision as it is crucial for the normal vitamin A metabolism in the retina of the eye. It also supports healthy bones, joints, and muscles.
Kelp leaves and stem
Seaweed has long been known to contain beneficial trace minerals, including iodine, which supports thyroid health. Iodine may also support normal cognitive function, metabolism, and skin health.
Thyme leaves
It may be called Thymus vulgaris, but there’s nothing offensive about this botanical. A member of the mint family and a cousin of oregano, thyme’s many constituents offer health benefits to the immune and digestive systems. It also has been used traditionally for respiratory tract support, including cough expectoration.
Thyme’s active constituents include monoterpenes such as thymol, limonene, carvacol, gamma terpinene, plus tannins, flavonoids, and triterpenes.
Thyme is native to the Mediterranean region, and Romans were known to eat it to ward off food poisoning. Before the onset of refrigeration, people regularly cooked with thyme to help protect against spoilage. According to research, the active constituent thymol provides antioxidant and immune-modulatory benefits.
Click here to access the factsheet